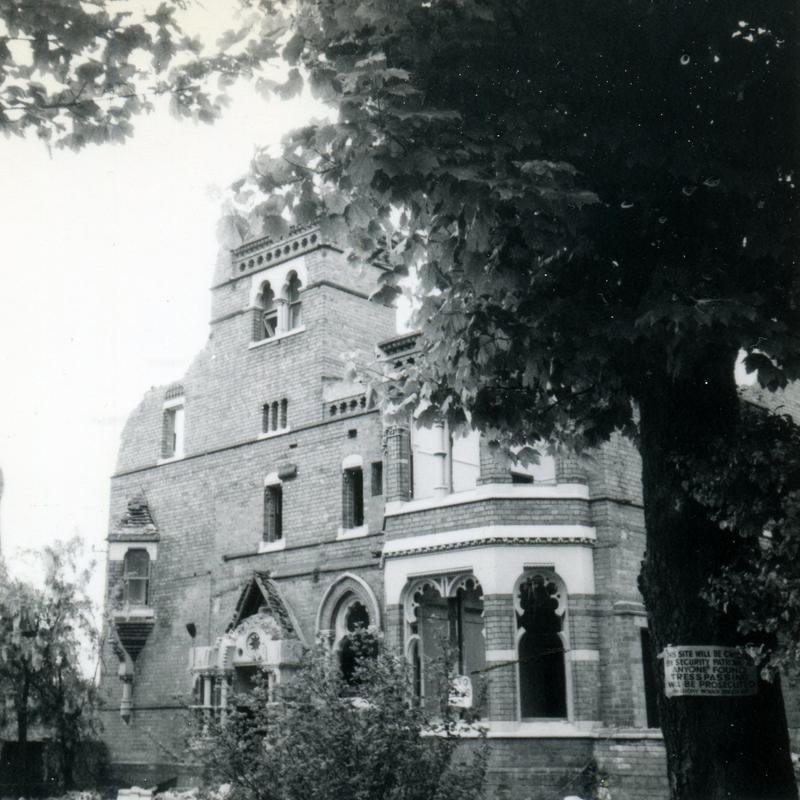
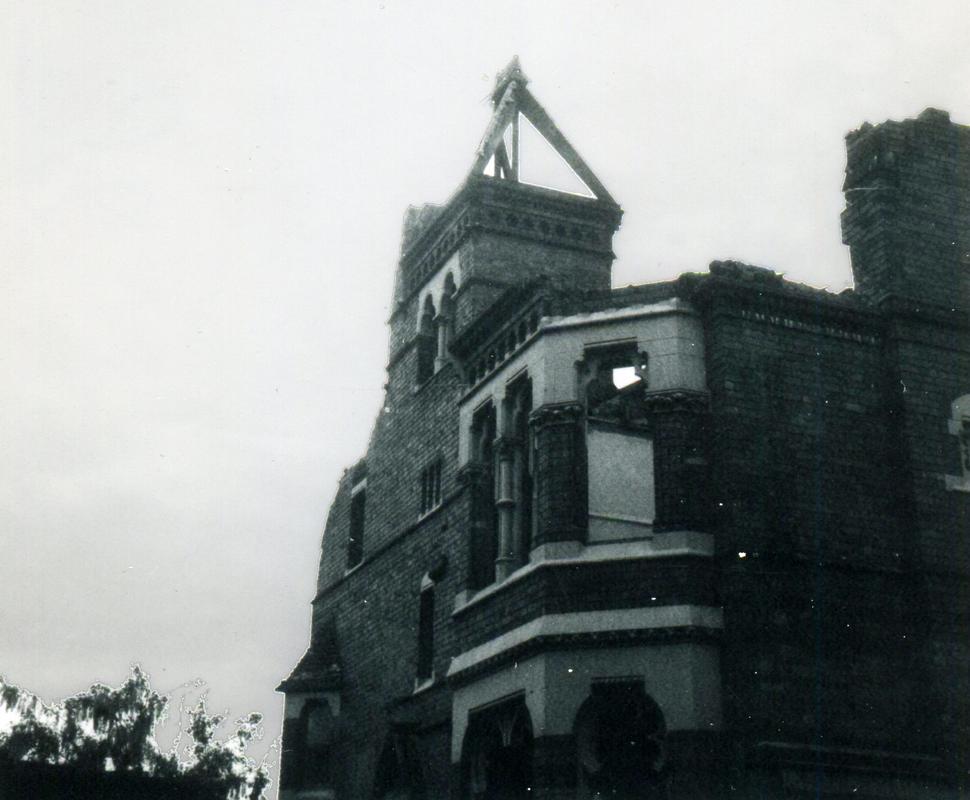
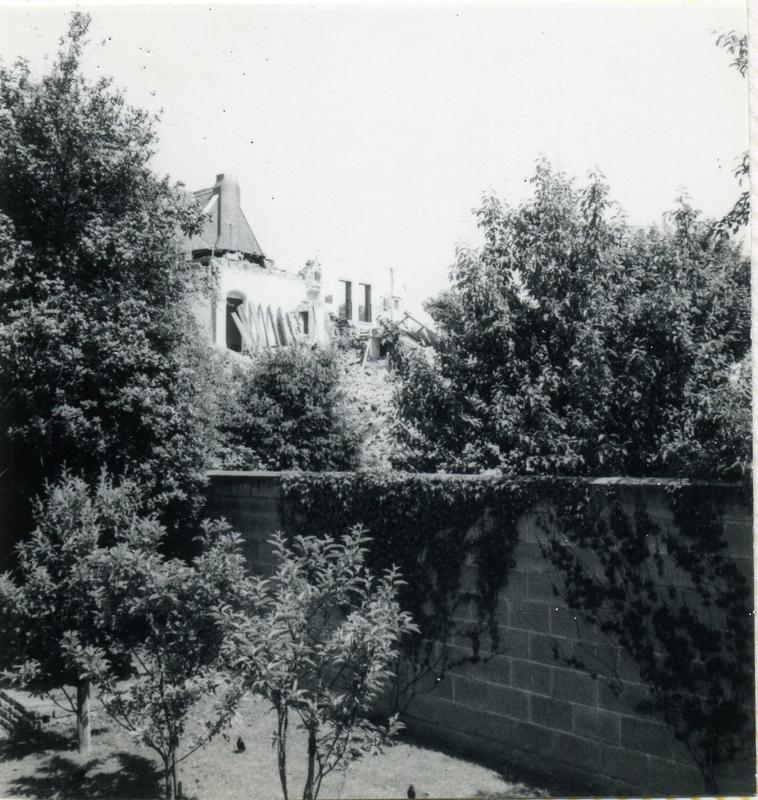
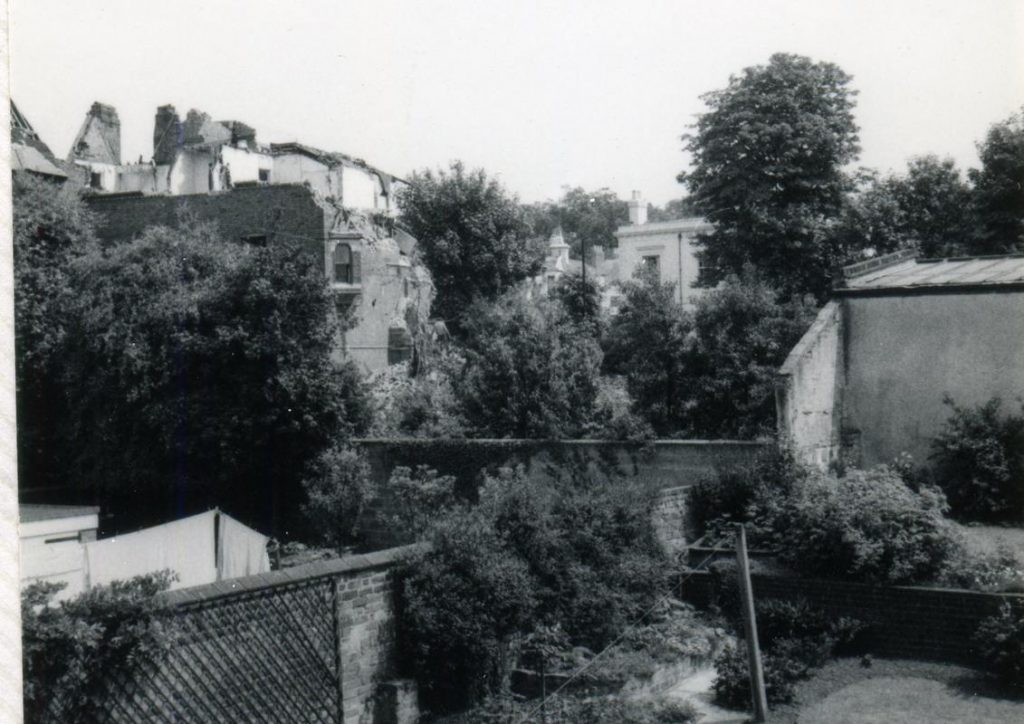
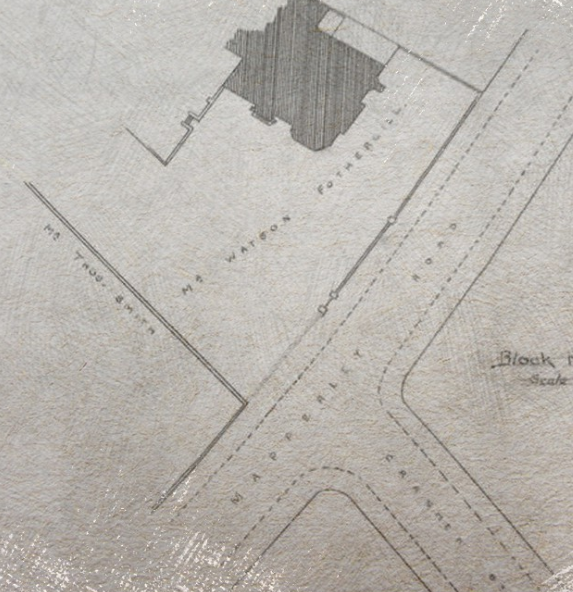
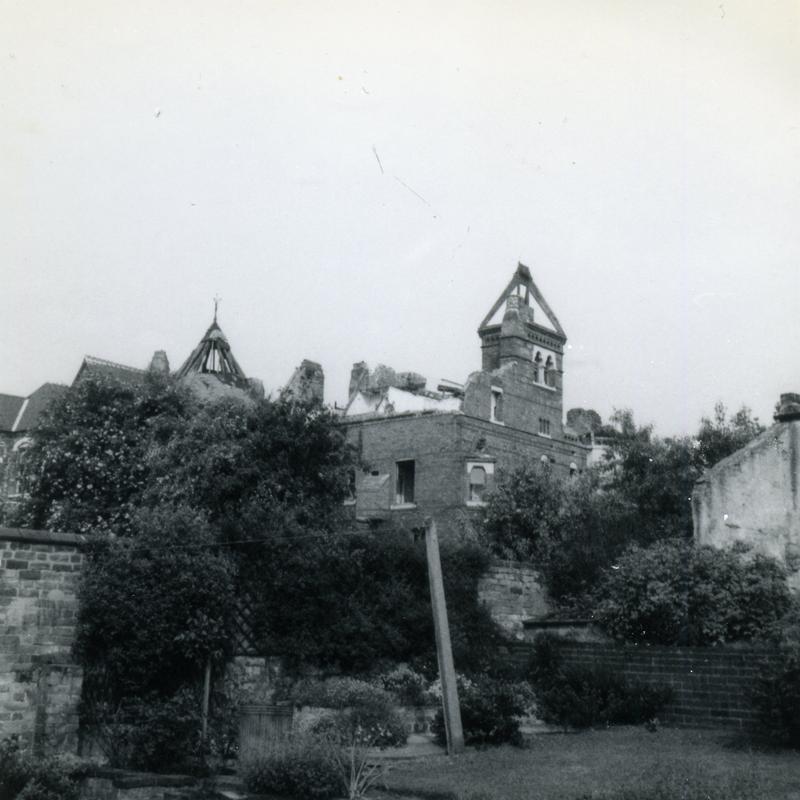The earliest house that architect Watson Fothergill (born Fothergill Watson, 1841) is known to have built is the dwelling he designed for himself and his family, which stood at 7 Mapperley Road, Nottingham.
Fothergill noted in his diary in 1870: “This Autumn after searching all over town for a site we liked I bought a piece of land on the northern side of Mapperley Road in Mr Patchitt’s estate.” Edwin Patchitt (1807-1888) was a solicitor and also a member of the Notts County Cricket team; he was Mayor of Nottingham for two terms between 1858 and 1860 and was the Secretary to the Enclosure Commissioners. He owned a triangle of land between Woodborough Road, Mansfield Road, Redcliffe Road and Elm Bank. Costing Fothergill £375, the land comprised 1,250 sq. yds and had a frontage of 105ft to Mapperley Road.
The first brick was laid on 3rd March 1871, and the Fothergill Family, which at this time comprised Fothergill, his wife Anne and their daughters Marion, Annie Forbes, and Edith Mary, moved from the house they had been renting on Hampden Street on 26th March 1872, “though the workmen were not yet out of it.”
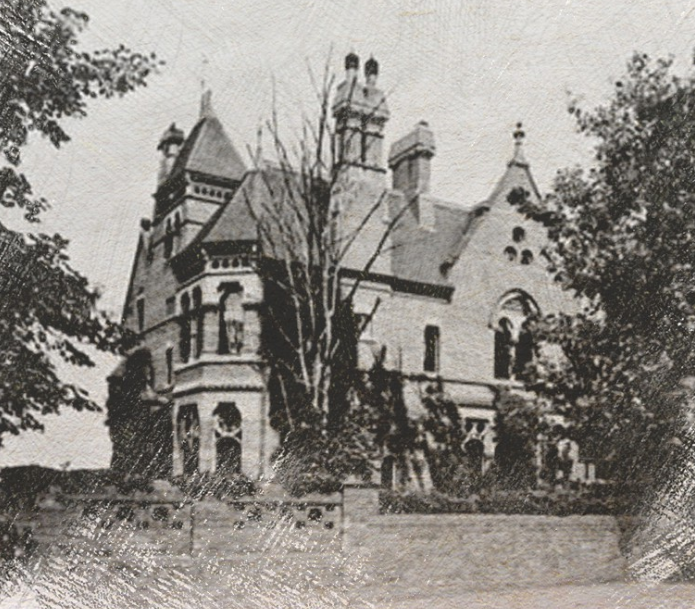

No drawings are known to survive of the original plan for the house, and there are few photos. I asked Nottingham-based architect and historic building consultant Peter Rogan to help me imagine what the house would have been like…
The house reflected High Victorian style with its asymmetry, individualism and accentuated features: brick with terracotta and stone details, prominent tall chimneys, and a four storey tower with decorative brickwork and a steep pitch roof. The house had an eclectic mix of window types: some sashes with stone lintels, bays and some with tracery. An entrance porch on the south-western side had slender decorative columns, above it an archway with a stone tympanum pieced by a window in the form of an eight-pointed star. On the side facing the road: trefoil decorations, circular windows and possibly a date stone. The gables made for broken rooflines creating a picturesque effect, capturing the light and shade that Fothergill found so alluring about the Gothic style.

In June 1872, Fothergill’s fourth child, Eleanor, was born: his three subsequent children, Samuel Fothergill 1874, Harold Hage 1877 and Clarice 1879, were also born here.
“The snuggest of houses! That is what we aimed at. Comfort, not great cold rooms, but gems of art sparkling round, an inviting home.”
Fothergill Family Record 1892.
Fothergill described the various features of the interior – sculptures, stag’s heads, green wallpaper in the style of Pugin, velvet curtains and tablecloths, and “modern” paintings on the walls. A brown wooden ceiling with gold details and floral decorations inscribed with a motto: “He that striveth for the mastery is temperate in all things.” (1 Corinthians 9:25) A portrait of Dr John Fothergill, his Quaker ancestor looked down on them from over the archway, and this was just the hall…
The rooms were adorned with brown silk and blue velvet, green walls and carpet, carved woodwork and decorated ceilings, but “everything is but a ground on which to display the pictures and the china” Among Fothergill’s collection of art works: a water colour interior of Salisbury Cathedral by JMW Turner and a St Cecilia by George Romney. (Links are guesses at the possible pictures, Fothergill is mentioned in catalogues of various exhibitions as he lent out the paintings, but I’ve got more research to do here!)
Around 1899 Fothergill added electric light and more bay windows to the house to provide light for displaying his collections of porcelain and Venetian glass.
“Indeed there is no doubt that the mediaeval style, call it old English if you will, in which both house and furniture are designed, does particularly lend itself to a home-like effect. It lacks but age, with a few ancestral traditions attached to it, to render it dear to us – no it cannot be more dear.”
Fothergill Family Record 1892.
In 1901, Fothergill purchased the adjacent land extending down to Chestnut Grove, from the lace merchant Thomas Birkin, it cost just over £1000. This became an ornamental garden and a tennis court.
When Fothergill died aged 87 in 1928, the house was sold and his art collection and the furniture was put up for auction, presumably so proceeds could be split between his five daughters, both his sons having failed to outlive him.

In the 1940s and 1950s, it appears that Councillor (later Lord Mayor) John Edwin Mitchell, lived at no. 7, then known as Park House (but I’m not 100% sure, as the numbering of the street has been altered).
Eventually the house was turned into flats, but it was demolished in 1968 – the value of the land too tempting to prevent developers from building many more dwellings on the site.

The present houses on the site were developed in the 1970s. They’re considerably less spectacular, but the development is at least called Fothergill Court!

The site of Fothergill’s house and more of his buildings in Mapperley Park, Sherwood Rise and Carrington will feature in my new walk, The Carrington Crawl. Dates will be announced as soon as the global situation allows… Meanwhile you can buy gift vouchers for yourself or friends and redeem them against future Watson Fothergill Walks with tour guide Lucy Brouwer.